How To Sharp The Food Industry: the Digital Responsibility Goals
The relationship between technology and our daily lives continues to evolve at a rapid pace. We are increasingly dependent on technological innovations to improve our quality of life. However, with this dependence comes a critical need to address the ethical implications of these advancements. In particular, the rise of generative AI and the integration of data into various sectors raise significant concerns about responsibility and privacy.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the intersection of technology and human rights, focusing on the challenges posed by generative AI and the role of digital responsibility goals (DRGs) in shaping a more ethical digital future. We’ll also discuss how these principles can be applied to the food industry to promote transparency and fairness.
Conversation’s BIG 3 takeaways:
- People do care about their data: 73% are concerned about their data being used without their agreement, and more than half of Europeans believe their digital rights are not adequately safeguarded.
- As customers, we all need to make deliberate decisions about the digital solutions we use. For example, adopting a more transparent nutrition app.
- The DRGs may become the new trend in the food and tech industries in 15 years, so jump on the train before its too late!
The Generative AI Boom: Opportunities and Pitfalls
Generative AI, including models like ChatGPT, Claude, and Gemini, represents a remarkable leap in technology for creativity and efficiency.
However, despite its benefits, generative AI also presents several challenges:
- Academic Integrity Issues: Educators have raised concerns about students using AI to complete assignments, undermining the learning process and creativity.
- Disinformation Risks: The ease with which AI can generate persuasive and seemingly credible content increases the potential for disinformation campaigns, affecting public trust and societal stability.
- Ethical Blind Spots: The rapid development of these technologies often outpaces ethical considerations. For example, there is no reliable way to detect whether a piece of content was AI-generated, complicating efforts to maintain authenticity and trust online.
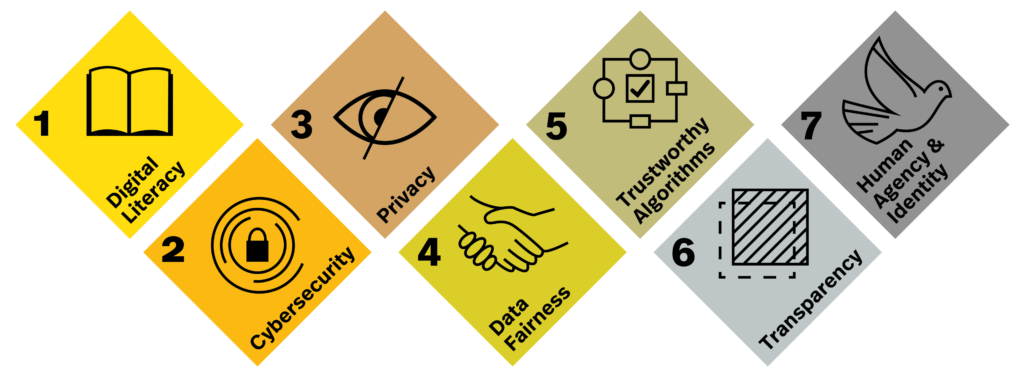
The Need for Digital Responsibility Goals (DRGs)
Digital Responsibility Goals (DRGs) are a set of 7 principles designed to guide the ethical development and use of technology. They aim to address the growing concerns about data privacy, cybersecurity, and AI fairness.
Applying the DRGs to the Food Industry
The Intersection of Data and Food
The food industry is increasingly leveraging data to improve efficiency and enhance consumer experiences. One notable example is Amazon’s Just Walk Out supermarket, which uses video recognition and data tracking to streamline the shopping process. While this innovation offers convenience, it also raises concerns about data privacy and surveillance.
- Efficiency and Convenience: Technology like Just Walk Out reduces the hassle of traditional checkout processes, saving time for consumers.
- Data Privacy Concerns: The extensive data collection required for such systems poses risks related to user privacy and data security.
Promoting Transparency and Fairness
The food industry can benefit from applying DRGs to address issues of transparency and fairness:
- Ingredient Transparency: Just as consumers should know what goes into their food, they should also be informed about how their data is used by digital platforms.
- Ethical Sourcing: Using DRGs to guide ethical sourcing and labeling practices can help ensure that consumers make informed choices about the food they purchase.
- Consumer Choice: By implementing DRGs, businesses can provide clearer information about their practices, allowing consumers to make more informed decisions and fostering a competitive market based on trust and ethics.
The Road Ahead for Digital Responsibility
While the concept of DRGs is promising, there are challenges to widespread adoption:
- Cost and Complexity: Implementing DRGs can be costly and complex, particularly for smaller businesses. There is a need for scalable solutions that can be adopted across different industries.
- Awareness and Education: Raising awareness about the importance of digital responsibility and educating both businesses and consumers is crucial for driving change.
- Regulatory Frameworks: Developing and enforcing regulations that support DRGs will be essential for ensuring that technology development aligns with ethical standards.
Conclusion
Generative AI offers exciting possibilities, but it also necessitates a thoughtful approach to prevent misuse and maintain trust.
Digital Responsibility Goals (DRGs) provide a valuable framework for guiding the ethical development and use of technology, ensuring that advancements serve the best interests of society.
In the food industry, applying DRGs can enhance transparency and fairness, ultimately leading to a more responsible and consumer-centric market. As we move forward, it is essential to continue advocating for and implementing these principles to build a digital future that is both innovative and ethically sound.
This article is based on an extended discussion on the Digital Food Podcast; tune in and educate your network!

